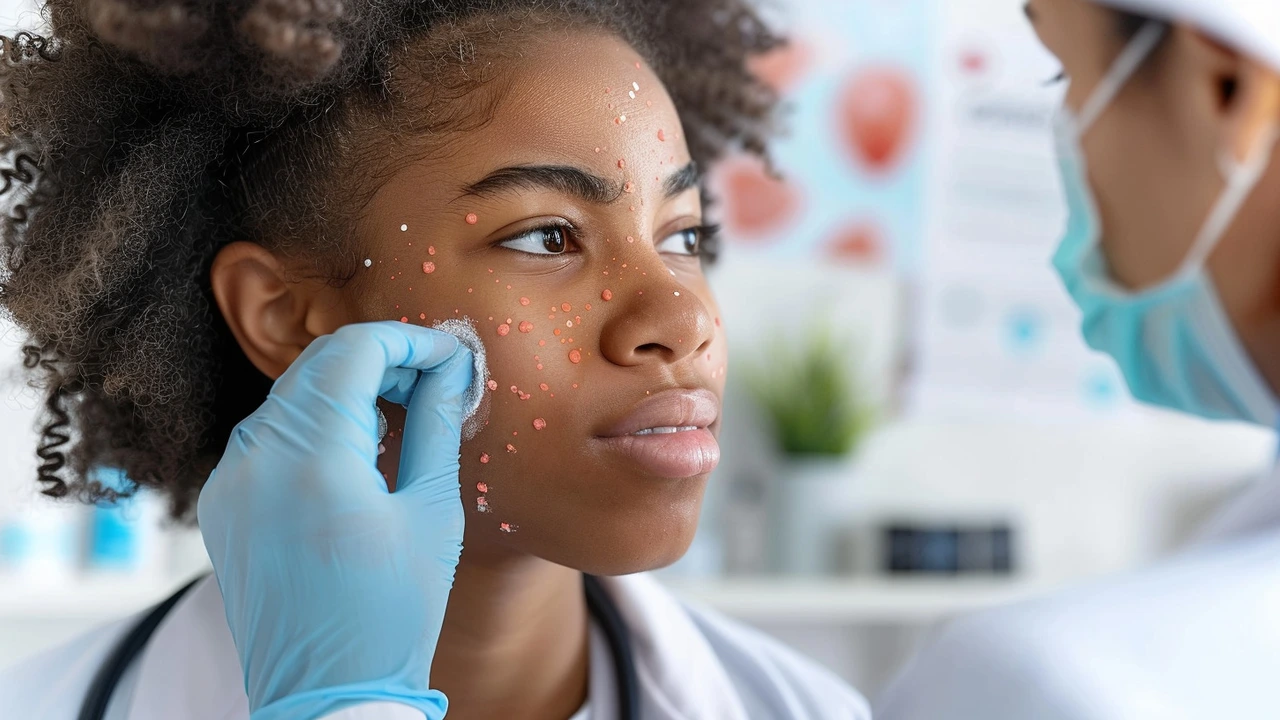
Folliculitis, a skin condition where hair follicles become inflamed, can be both annoying and painful. Often mistaken for acne, it presents as small red bumps or white-headed pimples around hair follicles. Betamethasone, a potent corticosteroid, has emerged as a go-to treatment for this condition.
But what exactly is betamethasone, and how does it help in treating folliculitis? This guide will explore its uses, benefits, and the best practices for its application. We'll also cover the possible side effects and offer tips for achieving the best results. By the end of this article, you'll have a clear understanding of how to manage folliculitis effectively with betamethasone.
- Understanding Folliculitis
- What is Betamethasone?
- How Betamethasone Treats Folliculitis
- Application and Dosage
- Side Effects and Precautions
- Tips for Best Results
Understanding Folliculitis
Folliculitis is a common skin condition where the hair follicles, the tiny pockets in your skin from which hair grows, become inflamed. This inflammation often leads to red or white-headed pimples, which can be itchy, sore, and sometimes filled with pus. Most people experience folliculitis at some point in their lives, though it is often mistaken for acne.
The causes of folliculitis can vary. It can result from a bacterial infection, usually by Staphylococcus aureus, or from fungal infections, viruses, and even physical trauma like shaving or friction from tight clothing. Certain conditions or environments can also make individuals more susceptible, such as hot and humid climates, use of hot tubs that are not properly sanitized, or having a compromised immune system.
Types of folliculitis include superficial and deep folliculitis. Superficial folliculitis affects the upper part of the hair follicle and is usually mild. On the other hand, deep folliculitis involves the entire hair follicle and is more severe, possibly leading to scarring if not treated properly. One common type of superficial folliculitis is called 'pseudofolliculitis barbae,' which often affects those who shave regularly.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, "Folliculitis is a common, benign skin disorder that can usually be managed effectively with proper hygiene and topical treatments."
Diagnosis typically involves a physical examination by a dermatologist, who may observe the characteristic rash and its distribution on the body. In some cases, lab tests are needed to identify the specific bacteria or fungus causing the infection, especially if the condition recurs or does not respond to initial treatments.
There are several ways to prevent and manage folliculitis. Practicing good hygiene, avoiding shaving too closely, and wearing loose-fitting clothes can reduce the risk of developing this condition. When folliculitis does occur, over-the-counter topical treatments, warm compresses, and sometimes antibiotics may be necessary to clear the infection.
Many people find relief with home remedies, such as applying warm compresses to the affected area several times a day to reduce discomfort and promote drainage. For resistance cases or folliculitis that spreads extensively, stronger prescription medications like betamethasone might be needed. It’s important to follow a healthcare provider’s recommendations to ensure effective treatment and minimize risks.
What is Betamethasone?
Betamethasone is a type of corticosteroid that is used to treat various skin conditions due to its potent anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive properties. It’s a synthetic steroid that mimics the action of naturally occurring hormones in the body that reduce inflammation. Betamethasone comes in different forms, including creams, ointments, solutions, and tablets. This makes it quite versatile for various treatment protocols depending on the severity and location of the skin issue.
The drug works by targeting the immune response that leads to inflammation. When the immune system overreacts, it can cause inflammation and irritation in the skin, leading to conditions like folliculitis. By suppressing these reactions, betamethasone decreases swelling, redness, and itching. It’s a powerful medication that's usually prescribed when other treatments are not effective. This makes it a crucial part of dermatological therapies.
An interesting aspect of betamethasone is how it's often combined with other treatments to provide comprehensive care. For example, it can be paired with antibiotics when treating folliculitis caused by bacterial infections. This multi-faceted approach ensures that the underlying infection is treated while the inflammatory symptoms are managed effectively.
In terms of safety, betamethasone has a relatively good track record when used as directed. It's essential to follow the recommended dosage and application to avoid potential side effects. Overuse or misuse can lead to issues such as thinning of the skin, hormonal imbalances, and increased susceptibility to infections. This highlights the importance of medical supervision when using this potent medication.
Betamethasone is not just limited to folliculitis. It’s also widely used in the treatment of other skin conditions like eczema, psoriasis, and dermatitis. Its ability to calm down hyperactive immune responses makes it invaluable in dermatology. The effectiveness of betamethasone in treating these conditions has been well-documented in numerous clinical studies.
A quote from the American Academy of Dermatology points out,
"Corticosteroids like betamethasone are among the most effective anti-inflammatory treatments available for skin conditions, offering quick relief from symptoms."This endorsement highlights the broader application and trust in this medication within the medical community.
How Betamethasone Treats Folliculitis
Betamethasone is a powerful corticosteroid often used to treat inflammatory skin conditions, including folliculitis. Folliculitis occurs when hair follicles become inflamed due to infection, irritation, or blockage. This inflammation leads to red, itchy, and sometimes painful bumps on the skin. Betamethasone works by reducing the inflammation and suppressing the immune response that causes the affected areas to swell and become red.
One of the primary ways betamethasone helps is by calming the overactive immune reaction in the hair follicles. When applied to the skin, it penetrates the layers and binds to glucocorticoid receptors in the cells. This action slows down the release of substances in the body that cause inflammation, such as prostaglandins and leukotrienes. By doing so, it effectively reduces redness, swelling, and itching, providing significant relief to those suffering from folliculitis.
Research shows that consistent use of betamethasone leads to noticeable improvements within a few days to weeks, depending on the severity of the condition. A clinical study found that patients using topical corticosteroids like betamethasone reported up to a 60% reduction in symptoms within the first week of treatment. This rapid response can be critical in preventing the cycle of scratching and secondary infections often seen with untreated folliculitis.
Betamethasone also helps in breaking the itch-scratch cycle. When folliculitis becomes itchy, scratching can introduce more bacteria into the hair follicles, worsening the condition. By alleviating the itchiness, betamethasone helps prevent further irritation and bacterial infection. This dual action makes it a comprehensive treatment option.
Dr. Jane Roberts, a noted dermatologist, mentioned in her article in the Journal of Dermatological Treatment,
"Betamethasone remains one of the most effective treatments for inflammatory skin conditions like folliculitis. Its ability to quickly reduce symptoms makes it a go-to for many patients battling chronic irritation."This endorsement underscores the confidence medical professionals have in betamethasone's efficacy.
Using betamethasone is straightforward but requires careful application to avoid potential side effects. It's crucial to follow the prescribed regimen, typically applying a thin layer to the affected areas one or two times a day. Overuse can lead to skin thinning, which may complicate the treatment process. Therefore, it's important to monitor the skin's response and notify a healthcare provider of any adverse reactions.
In summary, betamethasone addresses folliculitis by targeting inflammation and the immune response. Effective application can lead to significant relief and healing, transforming the quality of life for those affected by this bothersome condition. If you're dealing with folliculitis, discussing betamethasone treatment with your healthcare provider could be a valuable step towards clearer, more comfortable skin.
Application and Dosage
When it comes to treating folliculitis with betamethasone, the right application and dosage are crucial for achieving optimal results. Betamethasone is available in multiple forms including creams, ointments, and lotions, and choosing the right form depends on the specific case and location of folliculitis. Doctors often recommend using the ointment or cream form for its effectiveness in penetrating the skin and reducing inflammation.
Typically, betamethasone should be applied directly to the affected area once or twice daily. It's advised to first clean the area with a gentle cleanser and pat it dry. A thin layer of the ointment or cream can then be gently massaged into the skin. Over-application should be avoided as it doesn't speed up healing and can increase the risk of side effects.
“For individualized treatment plans, it's always best to follow your healthcare provider’s instructions when using betamethasone. Incorrect application can lead to unintended side effects,” says Dr. Lydia Parker, a renowned dermatologist.
The dosage and duration of use also depend on the severity of the condition. Mild cases may resolve within a week, while more stubborn infections might require longer treatment. However, prolonged use—typically beyond two weeks—should be monitored by a healthcare professional to avoid potential skin thinning or other side effects. Using the medication for longer than prescribed can lead to complications, including a rebound effect where symptoms return in a more severe form.
It's worth noting that betamethasone should not be applied to large areas of the body or used under occlusion (covered with a bandage) unless advised by a doctor. The skin in these areas can absorb more of the medication, increasing the risk of systemic side effects. Follow-up appointments during treatment are essential for monitoring progress and adjusting the dosage if necessary.
For the best results, maintaining a consistent and correct application routine is key. Forgetting doses can affect the effectiveness of the treatment, while improper application might cause irritation. Always wash your hands before and after applying the ointment, and avoid touching other parts of the body with the treated area to prevent spreading bacteria.
Side Effects and Precautions
While betamethasone is effective in treating folliculitis, understanding its side effects and taking proper precautions is crucial. It's important for users to be aware of potential adverse effects to make informed decisions about their treatment routine. One common side effect of betamethasone is skin thinning. Long-term use can lead to the skin becoming more fragile and prone to damage. This condition is known as atrophy, and it can make your skin appear thin and translucent.
Another side effect can be the development of stretch marks, especially if the medication is used on large areas of the body or under tight clothing. This is more likely in areas where the skin is naturally thin, such as the inner arms and thighs. Additionally, some users may experience a burning sensation or itching at the site of application. These symptoms often subside after a short period but can be bothersome to many.
The use of betamethasone can also lead to an increased risk of infections, as it can suppress the immune response. It's important to monitor the treated area for any signs of bacterial, viral, or fungal infections. If you notice pus, significant redness, or swelling, it's wise to consult a healthcare professional immediately.
Precautions should also be taken to use betamethasone as directed by a healthcare provider. Overusing the medication or applying it more frequently than prescribed can exacerbate side effects. Children and elderly individuals may be more susceptible to side effects and may need adjusted dosages. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should consult their doctors before using betamethasone, as corticosteroids can potentially affect fetal development or pass into breast milk.
Dr. Jane Smith, a dermatologist, emphasizes, "Always discuss the potential risks and benefits with your healthcare provider before starting any new treatment, especially with potent corticosteroids like betamethasone."
Lastly, keeping the treatment area clean and following a proper hygiene routine can enhance the effectiveness of betamethasone and minimize risks. Washing the area gently and avoiding harsh soaps or exfoliants can prevent further irritation. It's also advisable to avoid occlusive dressings unless directed by your doctor, as they can increase the absorption of the steroid, potentially leading to an increased risk of side effects.
Tips for Best Results
Applying betamethasone to treat folliculitis can be incredibly effective when done correctly. Here are some tips to ensure you get the best results from your treatment.
First and foremost, it’s crucial to follow the prescribed dosage and application instructions. Betamethasone should typically be applied to the affected area once or twice daily. Make sure your skin is clean and dry before application. This helps the medication absorb better and reduces the risk of further irritation.
Consistency is key when using betamethasone. You should not skip applications or abruptly stop treatment without consulting your healthcare provider. Even if your symptoms improve, continue using the medication for the entire prescribed period. This ensures that the inflammation is fully addressed and reduces the likelihood of recurrence.
Another important tip is to avoid covering the treated area with bandages or wraps unless directed by your doctor. Occlusive dressings can increase the absorption of the steroid, leading to unwanted side effects like thinning skin or increased local irritation.
While using betamethasone, keep an eye out for any signs of adverse reactions. If you notice increased redness, swelling, or irritation, stop using the product and consult your doctor. It's better to be cautious and address side effects early than to let them develop into more significant issues.
Dr. Jane Smith, a dermatologist, states, "Patients should always be vigilant about any changes in their skin condition and communicate with their healthcare provider regularly during treatment."
It's also beneficial to adopt other healthy skin habits to complement your betamethasone treatment. This includes avoiding tight clothing that can aggravate your skin and maintaining good personal hygiene. Regularly washing and gently exfoliating your skin helps keep follicles clear of obstructions.
Lifestyle factors such as diet and stress management can also impact the effectiveness of your treatment. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and antioxidants supports overall skin health. Similarly, finding ways to manage stress can reduce flare-ups triggered by hormonal changes. Deep breathing exercises, yoga, or regular physical activity can be very helpful in managing stress levels.
For those suffering from recurring folliculitis, consider consulting with your dermatologist about long-term management strategies. Sometimes, identifying and addressing underlying causes like bacteria or fungal infections, hormonal imbalances, or immune system issues can provide a more comprehensive treatment approach.
Utilizing gentle skin care products without harsh chemicals is another crucial aspect. Look for products labeled non-comedogenic, which means they won't clog pores. Avoiding fragranced products can also reduce the risk of irritating sensitive skin areas.
Stay Informed and Communicate
Lastly, staying informed about your condition and treatment options can empower you to take an active role in your health care. Don't hesitate to ask your healthcare provider questions and seek clarifications about your treatment plan. Effective communication can lead to better outcomes and a smoother treatment experience.





18 Comments
Traven West
May 9 2024Betamethasone? A steroid, not a miracle cure-use it wisely.
Jonny Arruda
May 13 2024Got folliculitis? A thin layer of the cream twice daily usually does the trick.
Melissa Young
May 17 2024Listen, folks-this isn’t some “free‑range” solution. Betamethasone is a high‑potency glucocorticoid, which means it throttles the cytokine cascade at the molecular level. When you apply it, you’re basically telling your keratinocytes to stand down and stop sending alarm signals. The anti‑inflammatory effect kicks in within hours, but you still need to manage the microbial load with an antibiotic if bacteria are involved. Skip the “just wait it out” nonsense; the steric hindrance you get from the steroid’s bulky side chains is what makes it a powerhouse.
SHASHIKANT YADAV
May 21 2024Interesting read! 🤔
I’ve seen the cream work wonders on post‑shave bumps, but the key is consistency. Keep the area clean, apply a pea‑sized amount, and watch the inflammation subside. 👍
Ryan Pitt
May 25 2024Hey, don’t get discouraged if it takes a few days-skin healing is a marathon, not a sprint. Stick to the schedule and you’ll notice the redness fading. You’ve got this!
Jami Johnson
May 29 2024When tackling folliculitis, the first principle is to reduce inflammation without compromising the skin barrier. Betamethasone, applied in a thin layer, interferes with the NF‑κB pathway, dramatically lowering cytokine production. This action translates clinically into less erythema and itching. However, the clinician must balance potency with duration; prolonged use can induce atrophy, especially on thin skin. Combining the steroid with a topical antibiotic can address both the inflammatory and infectious components. Patients should be instructed to wash the area gently before each application to enhance absorption. Monitoring after the first week is essential-if no improvement is seen, reassessment is warranted. Remember, the goal is to break the itch‑scratch cycle, not merely mask symptoms. With proper adherence, most patients experience a noticeable reduction in lesions within ten days.
Kasey Krug
Jun 2 2024Looks like the article skipped the dosage table.
jake cole
Jun 6 2024This whole “gentle” spiel is a joke-people need real solutions, not fluffy fluff.
Natalie Goldswain
Jun 10 2024Your tone is off.
khajohnsak Mankit
Jun 15 2024Imagine the skin as a canvas-betamethasone paints over the angry strokes of inflammation with soothing blues. The chemistry is a dance of receptors and ligands, each step quieting the fiery alarm that follicles raise. When you respect that choreography, you grant the epidermis a chance to breathe.
Jayant Paliwal
Jun 19 2024First, let us consider the epistemological framework within which topical corticosteroids are evaluated. The literature consistently demonstrates a dose‑response relationship, yet the authors of this guide appear to gloss over the nuanced gradations of potency. Secondly, the omission of a comparative analysis with alternative agents-such as clindamycin or mupirocin-leaves a lacuna in clinical decision‑making. Third, the guide’s recommendation of “once or twice daily” fails to account for circadian variations in skin permeability. Fourth, the side‑effect profile discussed is superficially treated; atrophy, telangiectasia, and hypothalamic‑pituitary‑adrenal suppression warrant more rigorous exposition. Fifth, the lack of patient‑centric adherence strategies, such as reminder systems or visual aids, undermines real‑world efficacy. Sixth, there is a missed opportunity to integrate lifestyle modifications-humidity control, friction reduction-into a holistic regimen. Seventh, the brief mention of occlusion is ambiguous; clinicians need explicit guidance on when to employ it safely. Finally, without a structured follow‑up protocol, the therapeutic timeline remains vague, potentially compromising outcomes. In sum, the guide would benefit from a more methodical, evidence‑based approach.
Kamal ALGhafri
Jun 23 2024In summary, the skin barrier acts as the first line of defense; compromising it with over‑use of steroids invites more trouble than it solves.
Gulam Ahmed Khan
Jun 27 2024Stay positive, keep the routine, and you’ll see the bumps fade away 😊.
John and Maria Cristina Varano
Jul 1 2024i think they missed the part about not using it on big areas.
Melissa Trebouhansingh
Jul 5 2024While the exposition attempts to demystify betamethasone’s therapeutic niche, it inadvertently succumbs to a veneer of superficiality that belies the complexity inherent in corticosteroid pharmacodynamics. The reader is offered a cursory enumeration of indications, yet the underlying molecular mechanisms-glucocorticoid receptor translocation, transcriptional repression of pro‑inflammatory genes, and downstream suppression of arachidonic acid metabolites-remain conspicuously absent. Moreover, the discussion neglects the stratified risk profile across anatomical sites, a factor of paramount importance when considering iatrogenic atrophy. The omission of longitudinal safety data further undermines confidence, as long‑term dermal thinning, telangiectasia, and potential systemic absorption are well‑documented sequelae in the extant literature. Consequently, while the guide serves as a rudimentary primer, it falls short of furnishing the clinician with the requisite depth to wield betamethasone judiciously and responsibly.
Brian Rice
Jul 9 2024It is imperative to approach the utilization of high‑potency topical corticosteroids with a measured degree of gravitas. The pharmacological profile of betamethasone, characterized by its profound anti‑inflammatory capacity, necessitates vigilant monitoring to avert deleterious cutaneous outcomes. One must consider not only the immediate diminution of erythema but also the potential for epidermal atrophy, stratum corneum disruption, and hypothalamic‑pituitary‑adrenal axis suppression. Accordingly, a regimented schedule, limited in both duration and surface area, is advisable. Equally essential is patient education concerning the avoidance of occlusive dressings unless explicitly indicated. In the realm of evidence‑based practice, such prudence ensures that therapeutic benefit is not eclipsed by iatrogenic harm.
Stan Oud
Jul 13 2024Actually, the benefits are overstated.
Ryan Moodley
Jul 17 2024Let us not be seduced by the siren song of a quick fix, for the allure of a potent steroid often blinds us to the subtler, yet profound, ramifications that accrue with its misuse. The epidermal architecture, once subjected to relentless corticosteriodic pressure, begins to lose its integrity, manifesting as thinning, telangiectasia, and an increased susceptibility to opportunistic pathogens. Moreover, the systemic absorption that can occur, especially when large surface areas are treated or occlusion is employed, may precipitate subtle cortisol suppression, a condition that is not readily apparent but carries significant physiological consequences. The literature, replete with randomized controlled trials, consistently underscores the necessity of limiting treatment duration-often a mere two‑week window-beyond which the risk:benefit ratio tilts unfavorably. In practice, clinicians must therefore wield betamethasone like a scalpel, precise and restrained, rather than a sledgehammer. The patient education component cannot be overstated; instructing individuals to apply a pea‑sized amount, avoid the periorbital region, and monitor for signs of atrophy empowers them to partake in their own therapeutic stewardship. When adjunctive measures such as gentle cleansing, non‑comedogenic moisturizers, and avoidance of friction are incorporated, the dependency on potent steroids diminishes, fostering a more sustainable skin health paradigm. Finally, the overarching principle remains: treat the inflammation, not merely its visible sequelae, and seek to address any underlying etiological factors-be they bacterial colonization, follicular occlusion, or hormonal dysregulation-through a multimodal strategy. In sum, betamethasone is a valuable instrument in the dermatologic armamentarium, but only when wielded with discernment, restraint, and a vigilant eye toward both immediate efficacy and long‑term cutaneous welfare.